JavaScript is the language of the web. In the browser, it makes pages interactive: it responds to clicks, validates forms, fetches data, and updates the UI without reloading. On the server (Node.js), it also powers APIs, tooling, and automation.
This guide focuses on modern JavaScript fundamentals you need to build real beginner projects: variables and types, functions, arrays/objects, DOM + events, and async programming. If you want an even broader “start from zero” roadmap, see: Learn Programming from Scratch .
Beginner outcome
Build one small interactive page: read user input, update the DOM, keep a simple state object, and fetch data at least once with error handling.
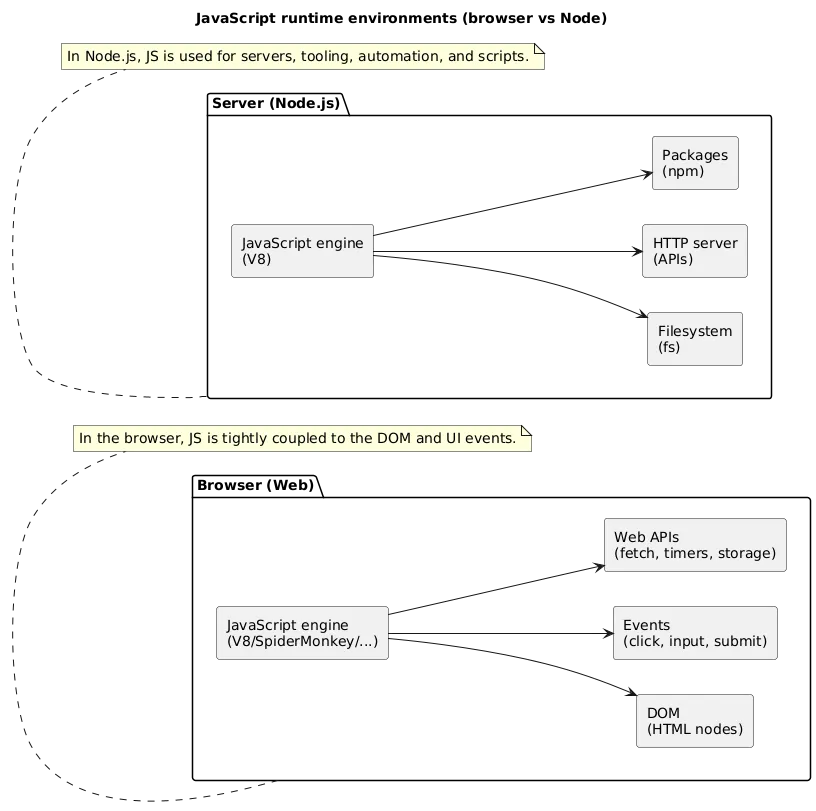
1. What JavaScript Is (And Where It Runs)
- Browser JavaScript: interacts with the DOM, events, storage, and network.
- Server-side JavaScript: runs on Node.js (APIs, scripts, tooling).
- Modern JS: uses modules, async/await, and better defaults (let/const).
2. Setup: Editor, DevTools, and Running Code
Keep your first setup minimal. You can learn a lot using a single HTML file and a script tag. Use your browser’s DevTools to inspect the DOM and debug code.
- Editor: VS Code (or any editor you like).
- DevTools: Console for logs, Sources for breakpoints, Network for fetch calls.
-
Run: start with a local HTML file and a linked
.jsfile.
<!-- index.html -->
<button id="btn">Click me</button>
<script src="app.js"></script>Common pitfall
If your script can’t “find” DOM elements, it often runs before the
page finished loading. Place scripts at the end of
<body> or listen for
DOMContentLoaded.
3. Variables: let, const, and (Avoiding) var
In modern JavaScript, you rarely need var. Use
const by default and let when reassignment
is required. This improves readability and prevents accidental bugs.
- const: default choice (prevents reassignment).
- let: use when you truly need reassignment.
- var: avoid in new code (function-scoped behavior is confusing).
const siteName = "All Days Tech";
let counter = 0;
counter += 1;
// siteName = "Other"; // TypeError in strict mode contextsPractical rule
If a variable represents a “thing” that should not be reassigned (a
config object, a DOM element, a base URL), declare it with
const.
4. Types, Coercion, and Operators (Beginner Traps)
JavaScript is flexible, which is helpful—but it can also surprise
beginners. The most common surprises come from:
type coercion, truthy/falsy, and the
difference between == and ===.
Core types
- Primitive: string, number, boolean, null, undefined, symbol, bigint
- Reference: object, array, function (they are objects under the hood)
Strict equality (always prefer ===)
console.log(0 == "0"); // true (coercion)
console.log(0 === "0"); // false (no coercion)Truthy / falsy quick map
// falsy values:
false, 0, "", null, undefined, NaN
// everything else is truthy:
"0", [], {}, "false", 1, -1Beginner trap
An empty array [] is truthy. If you need “has items”,
check arr.length > 0.
5. Control Flow: if/else, loops, truthy/falsy
Control flow is how you express decisions and repetition. Most real UI code follows a pattern: validate input → update state → re-render UI.
const score = 82;
if (score >= 90) {
console.log("A");
} else if (score >= 80) {
console.log("B");
} else {
console.log("C");
}Loops that matter most
- for...of for arrays
- forEach for simple iteration
- map/filter/find for transforming and querying arrays
const nums = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const doubled = nums.map((n) => n * 2);
const evens = nums.filter((n) => n % 2 === 0);
const firstBig = nums.find((n) => n > 2);6. Functions: Parameters, Returns, Scope, Closures
Functions help you keep code testable and maintainable. A useful mental model: event handlers should be small, and most logic should live in pure functions that return values.
const add = (a, b) => a + b;
function formatPrice(amount) {
return `€${amount.toFixed(2)}`;
}Scope basics (block scope with let/const)
if (true) {
const inside = "visible only here";
}
// console.log(inside); // ReferenceErrorClosures (why they matter)
A closure happens when a function “remembers” variables from the scope where it was created. This is common in UI code and event handlers.
function makeCounter() {
let count = 0;
return function () {
count += 1;
return count;
};
}
const next = makeCounter();
console.log(next()); // 1
console.log(next()); // 2Practical habit
Prefer small functions that do one thing and return a result. Keep DOM work at the edges (rendering + event handlers).
7. Arrays and Objects (Core Data Structures)
Arrays and objects are the backbone of most JavaScript programs. Arrays represent lists; objects represent structured records and “state”.
const user = { name: "Ada", role: "Engineer", active: true };
const tasks = [
{ id: 1, title: "Learn let/const", done: true },
{ id: 2, title: "Build a mini app", done: false }
];Destructuring (clean reading)
const { name, role } = user;
const [firstTask] = tasks;Mutation vs immutability (beginner-friendly rule)
In UI work, bugs often come from accidental mutation. When in doubt, create a new array/object instead of changing the existing one.
// create a new array with an added item
const nextTasks = [...tasks, { id: 3, title: "Ship", done: false }];
// create a new object with one field updated
const nextUser = { ...user, active: false };8. Modules: import/export Basics
Modules help you split code into files and reuse functions cleanly. In
the browser, ES Modules require
type="module".
<script type="module" src="app.js"></script>// utils.js
export function clamp(n, min, max) {
return Math.min(Math.max(n, min), max);
}
// app.js
import { clamp } from "./utils.js";
console.log(clamp(10, 0, 5));9. DOM: Select, Update, Render Patterns
The DOM is the browser’s representation of your HTML. JavaScript can select elements, update text, toggle classes, and create new nodes.
Select + update (core operations)
const titleEl = document.querySelector("#title");
titleEl.textContent = "Updated title";
const box = document.querySelector(".box");
box.classList.add("is-active");A simple “render from state” pattern
Beginners often update the DOM in many places, which becomes hard to maintain. A better pattern is: keep a single state and a single render() function.
const state = { count: 0 };
function render() {
const out = document.querySelector("#output");
out.textContent = `Count: ${state.count}`;
}
10. Events: Clicks, Inputs, Forms, Delegation
Events connect user actions to your code. Keep handlers small: read input → update state → render.
document.querySelector("#btn").addEventListener("click", () => {
state.count += 1;
render();
});Form handling (preventDefault + validation)
document.querySelector("#form").addEventListener("submit", (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const value = document.querySelector("#name").value.trim();
if (!value) {
console.error("Name is required");
return;
}
console.log("Submitted:", value);
});Event delegation (useful for lists)
If you render a list dynamically, attach one listener to the parent and detect which item was clicked. This scales better than adding listeners to every item.
document.querySelector("#list").addEventListener("click", (e) => {
const item = e.target.closest("[data-id]");
if (!item) return;
const id = Number(item.dataset.id);
console.log("Clicked item id:", id);
});11. Async JS: Promises, async/await, Fetch
Async code is everywhere on the web: network calls, timers, storage, and browser APIs. Promises represent a future result; async/await is syntax that makes promise-based code easier to read.
Fetch with error handling
async function loadUsers() {
try {
const res = await fetch("/api/users");
if (!res.ok) throw new Error(`HTTP ${res.status}`);
const users = await res.json();
return users;
} catch (err) {
console.error("Failed to load users:", err);
return [];
}
}Common async bug
If you forget await, you may accidentally work with a
Promise instead of real data. If you see
[object Promise], check your awaits.
12. Event Loop: Tasks vs Microtasks (Beginner Version)
JavaScript runs one piece of code at a time (single-threaded execution for your JS). Async callbacks are scheduled. Two queues matter most: task queue (timers, UI events) and microtask queue (promises).
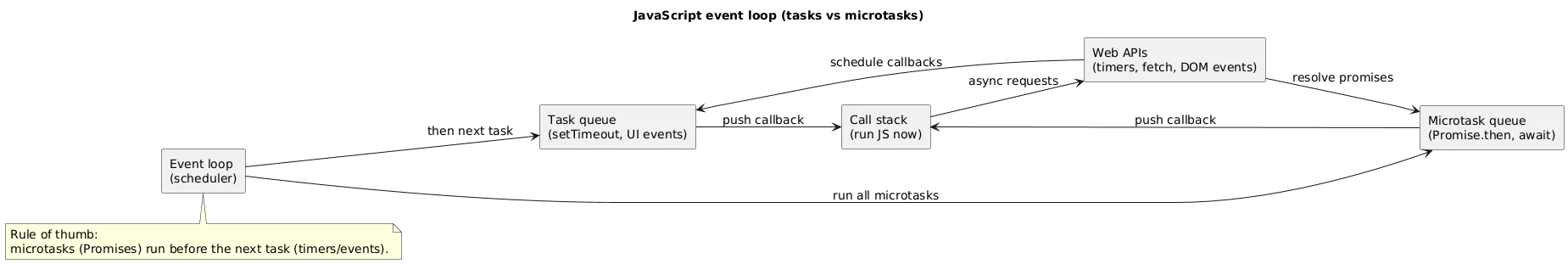
Microtasks vs tasks (quick demonstration)
console.log("A");
setTimeout(() => console.log("B (task)"), 0);
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log("C (microtask)"));
console.log("D");
// Typical output:
// A
// D
// C (microtask)
// B (task)13. Debugging: Console, Breakpoints, Common Errors
Debugging is a workflow. Use DevTools to inspect values and pause execution at the right moment. Aim to fix the root cause, not the symptom.
-
Console:
console.log(),console.error(),console.table() - Breakpoints: pause in Sources and inspect scope variables
- Network: verify fetch requests and response payloads
DOM null error
If querySelector returns null, your selector didn’t
match any element. Verify the selector, and ensure the script runs
after the element exists.
Common beginner errors (and what they usually mean)
- ReferenceError: variable doesn’t exist in the current scope.
- TypeError: cannot read property: you accessed a field on null/undefined.
- SyntaxError: parsing failed (missing bracket, comma, quote).
14. First Project Ideas + Build Checklist
The fastest way to learn is to finish small projects. Pick a project with clear input → logic → output, then iterate with one feature at a time.
Beginner-friendly projects
- Todo list: add/remove items, persist to localStorage, filter by done/undone.
- Quiz: track score, show results, reset state.
- Search + render: fetch from an API and render cards with loading + error states.
- Password generator: options (length, symbols), copy-to-clipboard.
Build checklist (copy/paste)
- UI: simple layout and clear controls.
- State: one “source of truth” object/array.
-
Render: a
render()function that updates UI from state. -
Events: handlers update state then call
render(). -
Async: at least one fetch with
try/catchand error UI. - Edge cases: empty input, network failure, empty results.
- Polish: remove noisy logs, keep helpful errors.
15. FAQ: JavaScript Basics
Do I need to memorize JavaScript syntax?
No. Focus on core concepts (state, functions, arrays/objects) and on learning DevTools debugging. Syntax becomes natural with repetition.
Why is async JavaScript important?
The web depends on network requests and event-driven flows. Understanding promises and async/await is essential to building real interactive apps.
When should I start using frameworks?
After you can build a small project with state, rendering, DOM events, and one async fetch call. Frameworks make more sense when you already understand the problem they solve.
What should I learn after basics?
Build two projects, then deepen: ES modules, fetch patterns, DOM rendering patterns, and finally a framework (React/Vue) depending on your goals. For general coding habits that scale, see: Clean Code Best Practices .
Key JavaScript terms (quick glossary)
- let / const
- Block-scoped variable declarations; const prevents reassignment.
- Strict equality (===)
- Compares value and type without coercion; preferred over ==.
- Type coercion
- Automatic conversion between types (common source of beginner surprises).
- DOM
- The Document Object Model: browser representation of HTML as a node tree.
- Event listener
- A function registered to run when an event occurs (click, input, submit).
- Promise
- An object representing a future value (resolved or rejected).
- async/await
- Syntax that makes promise-based async code easier to read and structure.
- Event loop
- Scheduling mechanism that decides when callbacks run (tasks vs microtasks).
Worth reading
Recommended guides from the category.
