Most AI value comes from unglamorous work: drafting, summarising, structuring messy information, and removing repetitive steps from everyday workflows. The winning pattern is consistent: AI produces a draft or options, and a human validates and approves. That approach keeps quality high and makes ROI measurable.
Best default mindset
Treat AI output as a draft, a proposal, or a checklist—not a source of truth. This single habit prevents most real-world failures (hallucinations, incorrect claims, accidental commitments).
1. What “practical AI” really means
“Practical AI” is not about chasing the newest model. It is about using AI where it reliably improves a workflow: speed (faster drafts), consistency (repeatable outputs), coverage (turning scattered inputs into documentation), and decision support (options, risks, assumptions, next steps).
- Practical use cases are measurable: time saved, fewer errors, faster turnaround, higher conversion, better resolution rate.
- Practical outputs are reviewable: bullet lists, structured templates, drafts, checklists.
- Practical workflows have guardrails: privacy rules, approval steps, and a rollback plan.
2. A simple scorecard: choose use cases that pay off
Use this scorecard to prioritize what to try first. Assign each dimension 1–5 and pick the highest totals. This keeps you away from high-risk, hard-to-validate tasks early on.
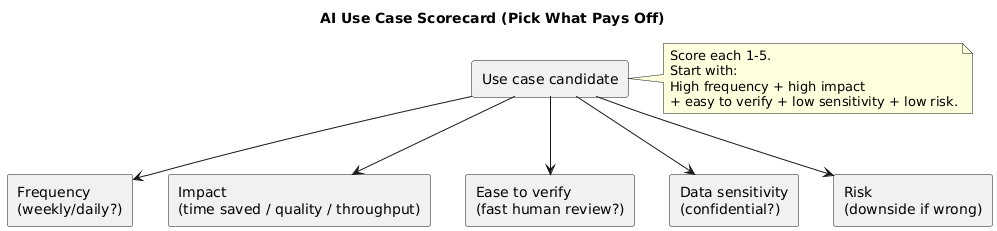
| Dimension | What to ask | What “good” looks like |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Do we do this weekly or daily? | Recurring work (emails, summaries, tickets, reports) |
| Impact | Does it remove meaningful effort or delays? | Saves time, reduces rework, improves consistency |
| Ease to verify | Can a human check correctness quickly? | Clear outputs with obvious errors |
| Data sensitivity | Do we need confidential data? | Low sensitivity or easy redaction |
| Risk | What happens if output is wrong? | Low downside; not legal/medical/financial commitments |
Best early use cases
Rewriting for clarity, meeting minutes, internal documentation, support drafts (with human review), and analytics narratives based only on provided facts.
3. Quick start: 7-day plan to get value fast
- Day 1: pick one workflow (high frequency + easy to verify) and define “success.”
- Day 2: create 3–5 reusable prompts and a template format (bullets/table/checklist).
- Day 3: run a small pilot on real tasks; track time and rework.
- Day 4: add guardrails (redaction rules, do-not-do list, approval step).
- Day 5: standardize outputs (SOP, email template, ticket macro, report structure).
- Day 6: measure ROI and failure modes; adjust prompts and inputs.
- Day 7: document the workflow and scale to a second similar use case.
4. Writing & communication (high ROI, low risk)
Writing is usually the safest entry point because humans can quickly review the result. High-impact use cases include: email drafts, tone rewrites, executive summaries, FAQs, and standard templates.
- Email drafting: clearer, shorter, more professional messages.
- Rewrite for tone: friendly, direct, executive, customer-facing.
- Summaries: convert long text into bullets and action items.
- Templates: SOPs, incident updates, project status notes.
- Localization: adapt to audience, not just literal translation.
Consistency trick
Ask for two versions: a short version (max 120 words) and a structured version (bullets + next steps). Combine the best parts.
5. Research & learning (faster understanding)
AI works well as a tutor and “question generator,” especially when you treat it as support rather than authority. Use it to explain, compare options, create study plans, and identify what you should verify.
- Explain at multiple levels: beginner, manager, engineer.
- Learning paths: 2–4 week plans with exercises.
- Question sets: flashcards, quizzes, interview questions.
- Decision matrices: pros/cons, trade-offs, risk lists.
Verification rule
For facts, numbers, legal details, pricing, or “latest” information—verify using primary sources. Use AI to speed up thinking, not to replace validation.
6. Meetings, notes & knowledge capture
AI is excellent at turning messy notes into usable artifacts: minutes, action lists, and lightweight documentation. The goal is not “perfect prose,” but less lost context.
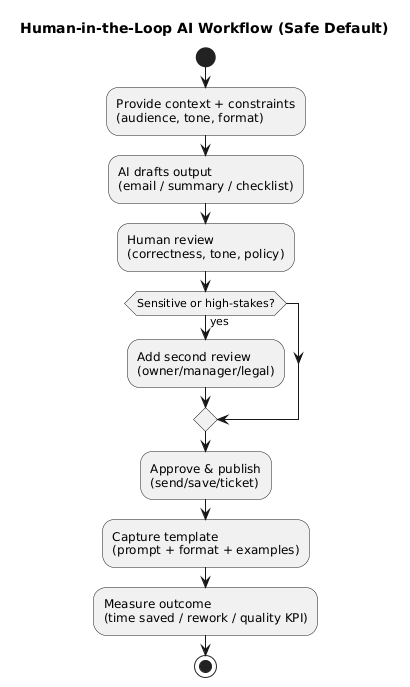
- Meeting minutes: decisions, action items, owners, due dates.
- Agenda creation: based on goals and open questions.
- Follow-ups: recap emails that clarify responsibilities.
- Internal FAQs: “how we do X” from recurring questions.
7. Customer support & helpdesk
The safest approach is “AI drafts, humans approve” for customer-facing messages—especially for refunds, policies, and commitments. Practical support workflows:
- Draft replies: consistent tone and structure.
- Ticket triage: summarize, categorize, propose routing.
- KB creation: convert solved tickets into help articles.
- Macros: reusable responses for common scenarios.
Support guardrail
Do not let AI invent policies, discounts, or refunds. Restrict it to approved knowledge and require review for sensitive cases.
8. Marketing & sales enablement
Marketing teams typically see fast wins in ideation, drafting, and formatting—provided claims are verified. AI works best when you give a short brand voice guide (tone, banned phrases, preferred terms).
- Campaign ideation: angles, hooks, audiences, messaging variants.
- Outlines: blog structures, landing page sections, FAQ blocks.
- Copy variants: multiple versions for tests (validate claims).
- Sales emails: personalization drafts from a customer profile.
- Positioning tables: draft comparisons (fact-check required).
9. Coding & IT workflows
AI can reduce friction for developers and IT teams in routine tasks: explanations, test scaffolds, runbooks, and debugging plans. Treat generated code as untrusted until reviewed and tested.
- Explain code: intent, edge cases, failure points.
- Draft boilerplate: tests, docs, config templates.
- Debugging support: hypotheses and step-by-step plans.
- Refactoring ideas: naming, structure, readability improvements.
- Runbooks: incident response checklists and SOP drafts.
10. Data analysis & reporting
AI is useful for turning numbers into a clear narrative when you provide the facts and explicitly forbid guessing. The best pattern is: facts in → structured report out.
- Explain metrics: define KPIs, interpret changes, list plausible drivers.
- Report drafts: executive summary + insights + recommended actions.
- Sanity checks: “what might I be missing?” and “what would you test next?”
- SQL help: draft queries (validate and run carefully).
11. Operations & admin automation
Operations is often the highest-leverage domain because work is process-heavy. Good use cases: SOP creation, checklist generation, handovers, policy summaries, vendor communication drafts.
- SOP creation: convert messy steps into clean procedures.
- Process improvement: identify bottlenecks and simplify flows.
- Checklists: onboarding, audits, launches, handovers.
- Vendor emails: clarify requirements, deliverables, timelines.
- Policy summaries: “what this means for me” versions.
12. HR & people operations
HR can benefit from more consistent documentation and clearer communication. Use strict privacy rules: redact sensitive employee details and rely on approved tools.
- Job descriptions: consistent structure, responsibilities, must-haves.
- Interview guides: competency-based questions and scoring rubrics.
- Training content: internal learning modules and quizzes.
- Employee comms: announcements, policy updates, onboarding docs.
13. Everyday personal use cases
Outside work, AI can help with planning and reducing “life admin” overhead:
- Meal planning: budget-based recipes and shopping lists.
- Travel planning: itineraries, packing lists, daily structure.
- Tutoring: explanations, exercises, practice questions.
- Personal writing: CV bullets, cover letters, bios.
- Decision support: compare options, list trade-offs, define next steps.
14. Safety, privacy & quality guardrails
Practical AI requires practical guardrails. Use this checklist before scaling any workflow:
- Data sensitivity: avoid confidential or highly personal data unless approved and protected.
- Accuracy: verify critical facts; prefer “list questions instead of guessing.”
- Attribution: draft original wording; avoid copying copyrighted text.
- Human approval: keep humans responsible for customer commitments and sensitive decisions.
- Logging: track prompts/templates versions and what changed when quality shifts.
Safe default
If the output could harm someone, cost money, or create legal/contractual obligations, require human review and validation every time.
15. Ready-to-copy prompt library (improved)
These prompts are designed to produce structured, reviewable outputs. Replace bracketed parts with your context. Add your company voice guidelines if relevant.
Rewrite an email for clarity and tone
Rewrite this email to be clear, friendly, and concise.
Audience: [customer / colleague / executive]
Tone: [neutral / warm / direct]
Constraints: keep under [120] words, keep all factual details unchanged.
Output: subject + email body.
Email:
[PASTE TEXT]Turn messy notes into minutes + action list
Turn these notes into meeting minutes.
Output sections:
1) Decisions
2) Action items (Owner / Due date)
3) Open questions
4) Risks & dependencies
Notes:
[PASTE NOTES]Summarise a long document into actions (no guessing)
Summarise the text below for a busy manager.
Rules: use only the provided text; if something is missing, list questions instead of guessing.
Output:
- 5-line executive summary
- Key points (bullets)
- Decisions needed
- Action items (Owner / Due date) - placeholders if unknown
Text:
[PASTE TEXT]Create an SOP from steps
Turn these steps into a clean SOP.
Include: Purpose, Scope, Preconditions, Step-by-step procedure, Inputs/Outputs, Common mistakes, QA checklist.
Steps:
[PASTE STEPS]Support draft with strict guardrails
Draft 2 customer support replies for the ticket below.
Rules:
- Do not promise refunds, policy exceptions, or timelines unless explicitly stated in the provided policy snippet.
- Ask 1-2 clarifying questions if required.
- Provide actionable troubleshooting steps.
Ticket:
[PASTE TICKET]
Policy snippet (optional):
[PASTE POLICY]Analytics narrative (facts-only)
Write a short report based only on the facts below.
If an explanation is uncertain, label it as a hypothesis and list what data would confirm it.
Output:
1) Executive summary
2) Key changes
3) Likely drivers (hypotheses)
4) Recommended next checks
Facts:
[PASTE METRICS / OBSERVATIONS]16. Implementation tips: from pilot to scale
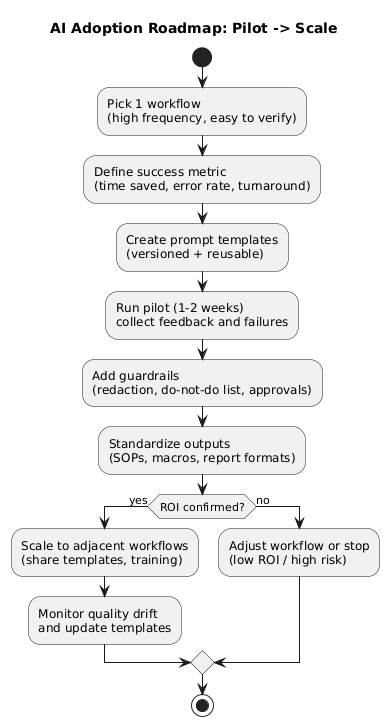
- Start narrow: one workflow, one output format, one success metric.
- Standardize prompts: version templates and keep a changelog.
- Add QA gates: approval steps, “do-not-do” list, and redaction rules.
- Measure ROI: time saved, fewer errors, faster delivery, improved consistency.
- Scale responsibly: expand to similar workflows and monitor quality drift.
17. Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most practical AI use cases for beginners in 2026?
Start with low-risk, easy-to-verify tasks: summarizing, drafting emails, rewriting for clarity and tone, brainstorming options, creating checklists, and turning messy notes into structured plans. These use cases deliver fast wins and are simple to review.
How can I use AI safely with company or client data?
Use organization-approved tools and policies, avoid pasting confidential details into public chats, and prefer workflows that redact sensitive data. Keep humans responsible for final decisions and validate critical facts with primary sources.
How do I measure ROI from AI tools in real workflows?
Define one workflow, set a baseline (time, error rate, turnaround), run a short pilot, and compare outcomes. Common ROI signals are time saved, fewer errors, faster delivery, improved consistency, and higher conversion or resolution rates.
What is the biggest mistake people make when using AI at work?
Treating AI as a source of truth. The best results come from using AI for drafts, structure, and options while humans verify details and approve outputs—especially for customer-facing commitments, legal, finance, or sensitive decisions.
Do I need advanced prompting to get good results?
No. Clear context, a defined audience, constraints (length, tone), and a requested format (bullets, table, checklist) usually produce strong results. Adding examples and review criteria improves quality further.
Key AI terms (quick glossary)
- Generative AI
- AI that creates content (text, images, code) based on patterns learned from large datasets.
- Prompt
- The instruction you give an AI tool to specify context, constraints, and output format.
- Hallucination
- When an AI produces confident output that is incorrect or not supported by evidence.
- Human-in-the-loop
- A workflow where a person reviews, validates, and approves AI output before it is used.
- Guardrails
- Rules and checks that keep AI usage safe: privacy rules, approval steps, do-not-do lists, and monitoring.
- ROI
- Return on investment—measured here as time saved, fewer errors, faster turnaround, improved consistency, or better outcomes.
Worth reading
Recommended guides from the category.