A RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) chatbot answers questions by combining two systems: retrieval (find the best knowledge-base passages) and generation (use an LLM to write a response grounded in those passages). When retrieval is strong and the prompt enforces grounding, hallucinations drop, answers become auditable, and your system can improve without re-training the model.
This guide walks you through a minimal, practical RAG setup with open-source tools: ingestion, chunking, embeddings, vector storage, retrieval tuning (filters + reranking), citations, follow-ups, evaluation, and production hardening. The focus is on choices that actually move quality in production—not just a demo that works once.
RAG success rule
If retrieval is weak, the LLM cannot save you. Invest first in clean ingestion, chunking, metadata, and retrieval tuning. Most “bad RAG” problems are retrieval problems.
1. What RAG is (and why it works)
- RAG retrieves: semantic search finds relevant chunks by meaning, not exact keywords.
- RAG grounds: the LLM is instructed to answer using only the provided context.
- RAG adds traceability: citations point to the sources used (doc + section + chunk).
- RAG updates easily: you can refresh the index as documents change—no retraining required.
- RAG scales operationally: you can measure retrieval accuracy and improve it iteratively.
2. Minimal RAG architecture (reference diagram)
A minimal RAG system has two pipelines: indexing (offline) and query (online). Keeping them explicit makes troubleshooting and scaling much easier.
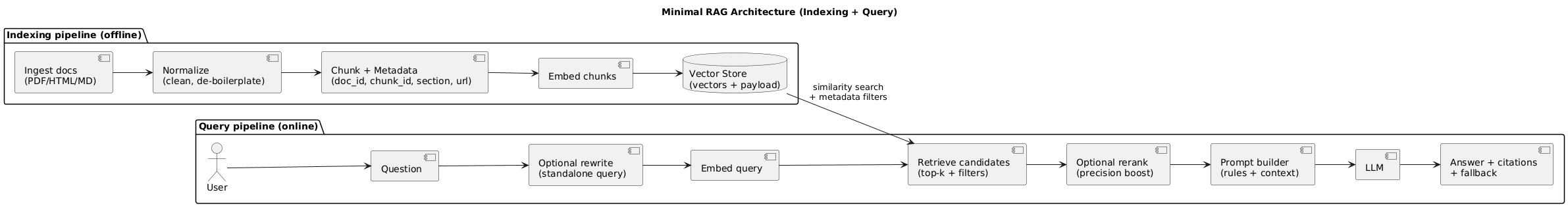
Indexing (offline)
Documents → Clean/Normalize → Chunk (+metadata) → Embeddings → Vector Store
Query (online)
Question → (optional rewrite) → Retrieve top-k (+filters) → (optional rerank)
→ Prompt (rules + context) → Answer + citations + fallback3. Open-source stack options (decision table)
You can build RAG with many combinations. Pick a stack that matches your constraints: dataset size, multi-user needs, deployment environment, and operational maturity.
| Component | Simple (local demo) | Practical (single service) | Production-ready (scalable) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LLM | Ollama (local) | Ollama / self-hosted | Self-hosted or vendor API behind a gateway |
| Embeddings | SentenceTransformers | SentenceTransformers | SentenceTransformers + batching + caching |
| Vector search | FAISS (in-process) | Chroma or Qdrant | Qdrant (service) + filters + replicas |
| API layer | Python script | FastAPI | FastAPI + auth + rate limits + observability |
Minimal “works today” stack
Local LLM (Ollama) + SentenceTransformers (embeddings) + Qdrant (vector DB) + a small FastAPI service.
3.1 Qdrant vs Chroma vs FAISS (quick guidance)
- FAISS: fastest path for small corpora and embedded deployments; you manage persistence and updates.
- Chroma: very approachable for prototypes; good developer experience; validate production requirements early.
- Qdrant: robust service model, strong filtering, operationally friendly when the app grows.
4. Step 1: Ingest and normalize documents
Great ingestion is mostly about consistency. Your goal is to create clean, stable text segments with reliable metadata, so retrieval quality stays predictable as your knowledge base evolves.
4.1 Ingestion checklist
- Extract text cleanly: remove navigation, repeated headers/footers, cookie banners, and boilerplate.
- Normalize: whitespace, broken lines, bullet lists, and unicode quirks.
- Preserve structure: headings, section titles, and original order.
- Attach provenance: source URL/path, doc title, section, updated_at, and a stable doc_id.
Ingestion → Chunking → Embeddings (diagram)
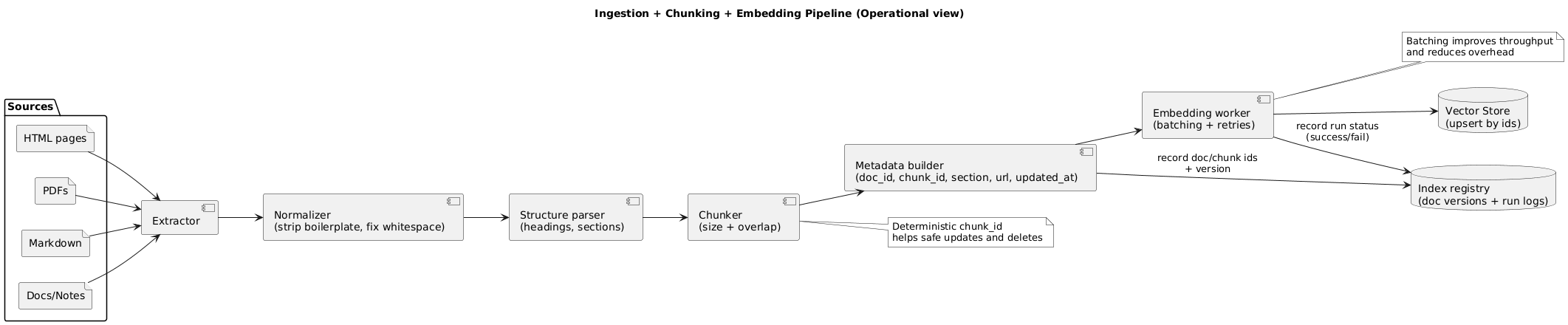
4.2 Versioning: plan for updates on day one
In production, documents change. Use deterministic IDs so you can upsert and delete safely: doc_id for the document, chunk_id for each chunk, and a doc_version or updated_at marker.
5. Step 2: Chunking strategy (settings that matter)
Chunking is the highest-leverage knob in RAG. Start with a sane baseline, then tune using retrieval metrics and real queries. Prefer structural chunking (headings/paragraphs) over raw character splits.
5.1 Recommended starter settings
| Setting | Starter value | When to change it |
|---|---|---|
| Chunk size | ~300–600 tokens | Smaller for FAQs and lists; bigger for technical explanations |
| Overlap | 10–20% | Increase if answers need cross-paragraph context |
| Top-k retrieve | 5–10 | Increase if coverage is low; decrease if context becomes noisy |
| Rerank candidates | 20–50 → rerank to 5–8 | Add rerank when many candidates look similar |
Chunking pitfall
Chunks that are too large reduce retrieval precision; chunks that are too small lose context and increase stitched answers. Tune chunking using questions your users actually ask.
6. Step 3: Create embeddings (model + batching)
Embeddings determine what “similar” means. Use one embedding model consistently for both documents and queries, and batch your embedding jobs to keep ingestion costs and latency manageable.
6.1 Practical rules
- Consistency: do not mix embedding models in one index unless you have a migration plan.
- Batching: embed chunks in batches for throughput; store results atomically (so partial runs don’t corrupt state).
- Deduplication: remove near-duplicate chunks to reduce index noise.
- Language awareness: if your corpus is multilingual, use embeddings that support your languages well.
7. Step 4: Store vectors + metadata (schema)
Your vector record should be debuggable. If you cannot explain why a chunk was retrieved, you will struggle to improve quality. Store enough metadata to filter, cite, and trace outputs.
7.1 Minimal payload schema
- ids: doc_id, chunk_id
- text: chunk_text (cleaned) + optional short snippet
- provenance: doc_title, section_heading, source_url/path
- controls: tags/category, tenant/team (if multi-tenant), updated_at, doc_version
7.2 Why metadata matters
- Filters: limit search to relevant product areas, teams, or dates.
- Citations: show where the answer came from.
- Debugging: identify which docs are causing noise.
- Governance: apply access control or retention rules per source.
8. Step 5: Retrieval (top-k, filters, hybrid, rerank)
Retrieval quality determines the ceiling of your system. You want to retrieve answer-bearing chunks reliably, not just “kind of related” chunks.

8.1 Retrieval controls that matter
- Filters: category/tag/product, tenant/team, and date windows (when docs change often).
- Hybrid search: combine lexical (BM25) with dense embeddings to improve recall for exact terms and IDs.
- Diversity: avoid retrieving 10 near-duplicates from the same paragraph.
- Reranking: rerank candidates to improve precision for ambiguous queries.
High ROI retrieval upgrade
Add metadata filters + reranking before changing the LLM. These two changes often beat “bigger model” upgrades.
9. Step 6: Grounded answer prompt + citations
Your prompt should enforce two behaviors: (1) cite evidence and (2) refuse to guess when evidence is missing. This is crucial for user trust and for reducing unsafe or misleading output.
9.1 A practical grounded prompt pattern
- Rules: answer only from context; if missing, say “insufficient context” and ask a clarifying question.
- Evidence format: provide chunk IDs or [Doc Title § Section] citations.
- Answer structure: short answer → steps/details → citations per section.
Answer format (example)
1) Short answer
2) Details / steps
3) Citations: [Doc §Section] or [chunk_id]
If evidence is missing: say so, then ask a clarifying question.9.2 Citations that users trust
- Cite the specific section, not just the entire document.
- Prefer citations near claims (“inline”) for factual statements and numbers.
- If retrieved context conflicts, show the disagreement and ask what source to prioritize.
10. Step 7: Follow-ups and conversation memory
Follow-ups are where many RAG demos break. A user asks “What about the second option?” and retrieval collapses because the query lacks nouns. The common fix is question rewriting: convert the follow-up into a standalone query before retrieval.
10.1 Practical approach
- Short-term memory: keep the last few user turns in the prompt.
- Rewrite step: turn follow-ups into standalone queries (“What about Qdrant?” → “Qdrant pros/cons for RAG vector store”).
- Retrieve every turn: do not rely only on the previous turn’s retrieved context.
- State with discipline: store only the minimal conversation state needed (avoid “infinite chat history”).
11. Step 8: Evaluate and improve quality
Evaluate retrieval and generation separately. If the answer is wrong, you need to know whether the model hallucinated or the system failed to retrieve the right chunk.
11.1 Metrics worth tracking
- Retrieval coverage: how often top-k contains the answer-bearing chunk.
- Grounding adherence: how often the answer stays within retrieved evidence.
- Citation quality: citations present, non-empty, and match the claims.
- Fallback correctness: “I don’t know” triggers when evidence is missing.
- Latency: end-to-end and per step (retrieve, rerank, generate).
Evaluation trap
If you only evaluate final answers, you won’t know if failures come from retrieval or the prompt/model. Always measure both layers.
11.2 A simple improvement loop
- Collect failed questions (with retrieved chunk IDs).
- Fix ingestion/chunking/metadata for those sources.
- Adjust retrieval (filters, top-k, hybrid, rerank).
- Adjust prompting (grounding rules, citation format, fallback).
- Re-run the eval set and track deltas.
12. Production hardening (security, privacy, monitoring)
Production RAG is not only “quality.” It is also access control, safe handling of sensitive documents, and protection against prompt injection through retrieved text.
12.1 Security and access control
- Authorization in code: enforce tenant/team filters server-side (never rely on the prompt).
- Least privilege: retriever can only access allowed collections; tools must be scoped.
- Auditability: log retrieved chunk IDs and doc IDs (not raw content) for debugging.
12.2 Prompt injection defense (RAG-specific)
- Treat retrieved content as untrusted input.
- Separate “instructions” from “evidence” in the prompt (clear delimiters and role separation).
- Prefer extractive quoting for sensitive answers (“According to context: …”).
12.3 Privacy basics
- Do not index sensitive documents without a policy, retention plan, and access controls.
- Redact or tokenize personal data before embedding where feasible.
- Keep short retention for caches and avoid logging raw prompts by default.
12.4 Monitoring for RAG
- Quality signals: citation rate, fallback rate, “no evidence” rate by category.
- Retrieval signals: top-k similarity scores, duplicate chunk rate, filter hit rates.
- Operational signals: latency by stage, errors, timeouts, index refresh failures.
13. Deployment checklist (local to production)
- Index refresh: scheduled re-ingest for changed docs; upsert by stable IDs.
- Observability: log query, retrieved chunk IDs, latency, and errors (avoid raw text by default).
- Access control: restrict sources by user/team/tenant where needed.
- PII handling: do not embed/index sensitive data without controls (redaction, retention, audits).
- Fallback behavior: “I don’t know” + clarify question + escalation path (optional).
- Rate limiting: protect the service and model runtime from abuse.
- Cost controls: cache embeddings for repeated queries; cap rerank candidates; cap context length.
14. FAQ: RAG chatbots
Can I run a RAG chatbot fully locally?
Yes. You can run a local LLM, local embeddings, and a local vector index or self-hosted vector database. Performance depends on your hardware and corpus size.
Do I need reranking for good RAG results?
Not always, but reranking often improves precision when many chunks are semantically similar. It is one of the highest-impact upgrades after fixing ingestion, chunking, and metadata.
What reduces hallucinations the most in a RAG chatbot?
Strong retrieval quality plus strict grounding rules: answer only from retrieved context, cite sources, and fall back to “insufficient context” instead of guessing.
How do I handle PDFs and messy documents for RAG?
Extract and normalize text carefully, remove repeated boilerplate, preserve headings, and chunk by structure where possible. Keep source metadata so you can debug retrieval quickly.
What metadata should I store for a RAG knowledge base?
At minimum: doc title, section heading, source URL/path, updated time, doc_id, and chunk_id. Metadata enables filters, provenance, and trustworthy citations.
Key RAG terms (quick glossary)
- RAG
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation: retrieve relevant passages, then generate an answer grounded in them.
- Embedding
- A vector representation of text that captures semantic meaning for similarity search.
- Vector database
- A system optimized for storing vectors and running similarity search with metadata filters.
- Chunk
- A smaller segment of a document (with metadata) used for retrieval and prompting.
- Top-k
- The number of retrieved chunks returned by the vector search step.
- Reranker
- A model that re-sorts retrieved candidates to improve relevance/precision.
- Grounding
- Constraining the model to answer using provided evidence (and cite it).
- Query rewriting
- Converting follow-up questions into standalone queries to improve retrieval.
- Hybrid search
- Combining lexical search (e.g., BM25) with dense embeddings for better recall and precision.
Worth reading
Recommended guides from the category.